Lung Fibrosis vs. COPD: Understanding the Differences

Lung diseases can significantly impact breathing and overall health, but not all conditions are the same. Two commonly confused respiratory diseases are lung fibrosis and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). While both affect lung function, their causes, progression and treatment options differ. Understanding these differences is crucial for early diagnosis and appropriate management.
What is Lung Fibrosis?
Lung fibrosis, also known as pulmonary fibrosis, is a condition where lung tissue becomes scarred and stiff over time, making it difficult to breathe. This scarring is often irreversible and worsens progressively. It can result from genetic factors, environmental exposures, autoimmune diseases, or infections.
Symptoms of Lung Fibrosis:
- Shortness of breath (especially during exertion)
- Chronic dry cough
- Fatigue and weakness
- Clubbing of fingers (in some cases)
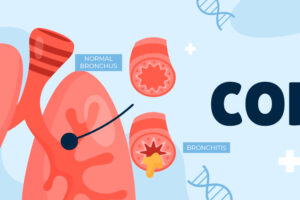
What is COPD?
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is a progressive lung disease that includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational hazards.
Symptoms of COPD:
- Chronic cough with mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Frequent respiratory infections
Key Differences Between Lung Fibrosis and COPD
| Feature | Lung Fibrosis | COPD |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Scarring of lung tissue | Airway inflammation and obstruction |
| Progression | Irreversible and worsens over time | Manageable with treatment |
| Symptoms | Dry cough, breathlessness | Mucus-producing cough, wheezing |
| Treatment | Lung fibrosis treatment involves oxygen therapy, medications, and possibly a lung transplant doctor | COPD treatment includes inhalers, medications, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation |
Treatment Approaches
For lung fibrosis treatment, options include antifibrotic medications, oxygen therapy, and in severe cases, a lung transplant. If fibrosis progresses despite treatment, consulting a lung disease specialist or pulmonologist can provide further options.
For COPD treatment, medications like bronchodilators, steroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation can help manage symptoms. A specialized COPD doctor can tailor treatment based on disease severity. In some cases, bronchoscopy may be performed to evaluate lung function and clear mucus build-up.
Final Thoughts…
Understanding the differences between lung fibrosis and COPD ensures the right treatment path and better disease management. If you or a loved one needs expert care, consult a pulmonologist today.
Looking for pulmonologist in Secunderabad? COPD Specialist or Lung Fibrosis doctor in Secunderabad? Contact us to book an appointment.