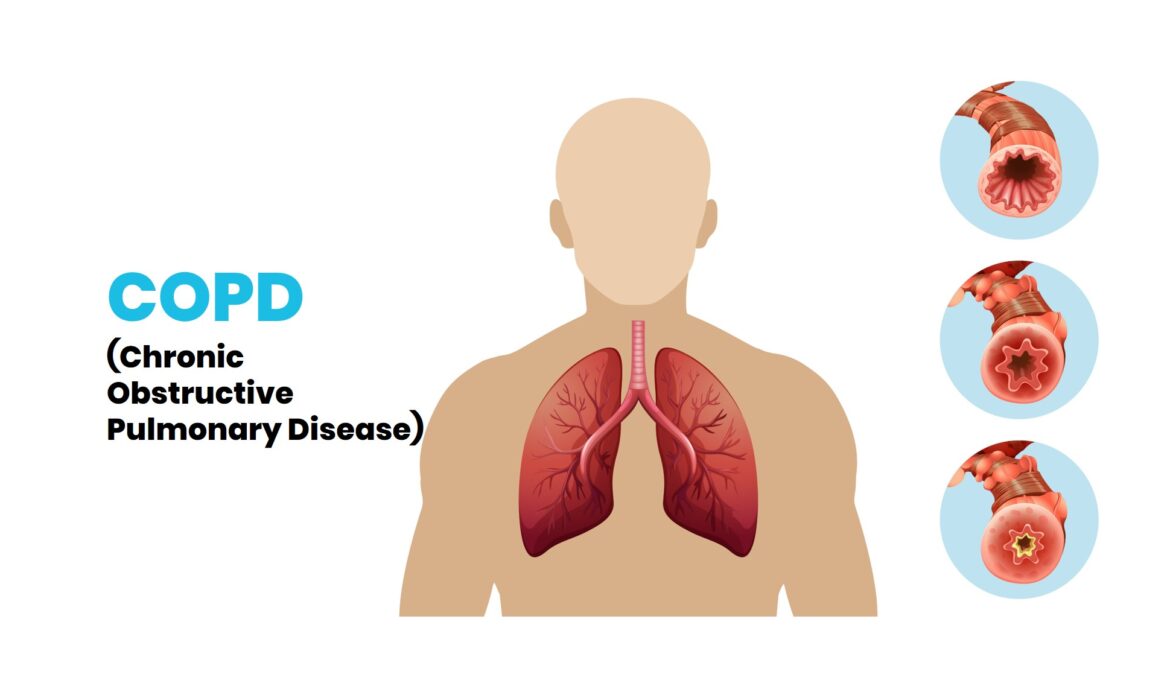
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease ( COPD ) is the among the top three causes of death world-wide and 90% of these death occurs in low and middle income countries. Current statistics showed that more than 3 million died of COPD in 2012 which accounts for 6% of all death globally.
COPD is a common, preventable and treatable disease that is characterised by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation that is caused by significant exposure to gases or noxious particles.
What are the symptoms of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
It is characterised by long history of shortness of breath.
Chronic cough with sputum production
History of exposure to Smoke or occupational exposure
How to diagnose COPD?
COPD should be considered in any patient who has dyspnoea, chronic cough and sputum production and with a history of exposure to risk factors for the disease.
Spirometry is required to make the diagnosis of COPD in the clinical context and post bronchodilator FEV1/FVC < 0.70 confirms the presence of perform airflow limitation.
Based on the spirometry , it was graded from mild to very severe based on FEV1.
What are the treatment options for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
Smoking cessation is the mainstay of treatment as it has the greatest capacity to influence the natural history of COPD
Influenza and Pneumococcal vaccination at regular interval
Pharmacological therapy by metered dose inhaler and nebulisations is an important aspect of treatment to reduce symptoms and frequency and severity of exacerbation and to improve exercise tolerance and heath status.
There are different classes of drugs for the treatment which is as follows: